By: Team T13-2 Since: Nov 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Viewing help :
help - 3.2. Adding a staff:
add - 3.3. Listing all staff :
list - 3.4. Editing a staff :
edit - 3.5. Deleting a staff :
delete - 3.6. Selecting a staff :
select - 3.7. Giving feedback to a staff:
feedback - 3.8. Rating a staff:
rate - 3.9. Setting private fields:
privacy - 3.10. Locating staff by name:
find-n - 3.11. Locating staff by email:
find-e - 3.12. Locating staff by department:
find-d - 3.13. Locating staff by manager:
find-m - 3.14. Sorting all staff by name :
sort - 3.15. Sorting all staff by department :
sortDept - 3.16. Sorting all staff by rating :
sortRatingDown - 3.17. Sorting all staff by rating :
sortRatingUp - 3.18. Favouriting a staff :
favourite - 3.19. Unfavouriting a staff :
unfavourite - 3.20. Listing entered commands :
history - 3.21. Undoing previous command :
undo - 3.22. Redoing the previously undone command :
redo - 3.23. Counting the number of staff [coming in v2.0]:
count - 3.24. Locking SSENISUB [coming in v2.0]:
lock - 3.25. Unlocking SSENISUB [coming in v2.0]:
unlock - 3.26. Authorization levels for features [coming in v2.0]:
login,logout - 3.27. Encrypting data files [coming in v2.0]
- 3.28. Clearing all entries :
clear - 3.29. Saving the data
- 3.30. Exiting the program :
exit
- 3.1. Viewing help :
- 4. FAQ
- 5. Command Summary
1. Introduction
SSENISUB is intended for organizations who follows a strict hierarchical structure to manage their manpower and allows the staff to use this as contact book.
Jump to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started. Enjoy!
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java version
9or later installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
SSENISUB.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for SSENISUB software.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
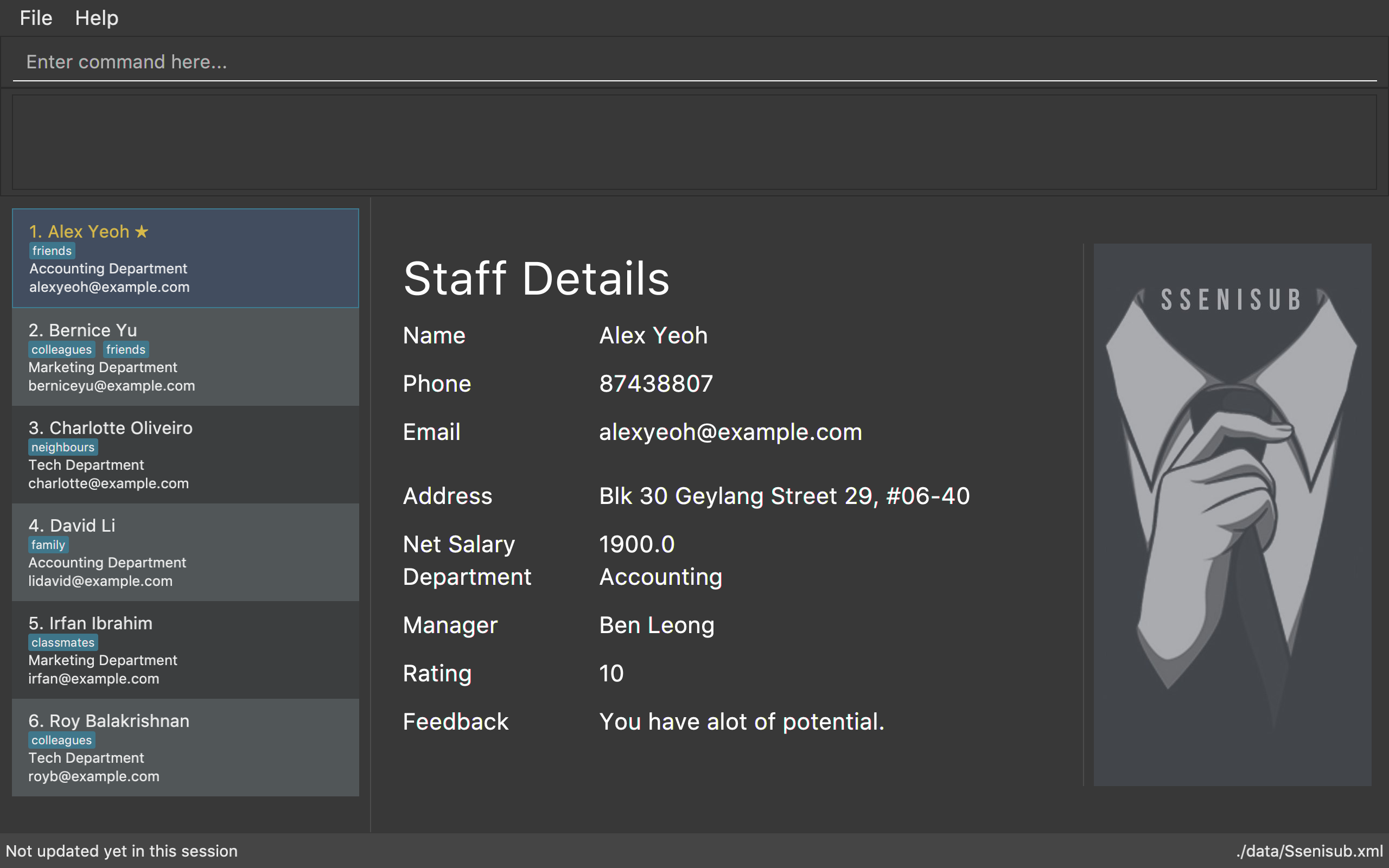
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
list: lists all staff -
addn/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John Street Blk 123, #01-01 d/Tech m/Alice Tan: adds a staff namedJohn Doeto SSENISUB. -
delete3: deletes the 3rd staff shown in the current list -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for details of each command.
3. Features
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/staff,t/manageretc. -
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Adding a 'p' infront of the parameter private. e.g. pp/PHONE makes the phone number private to the other user.
-
Only
PHONE,EMAILandADDRESSfields can be initialized as private.
Fields restrictions
NAME |
Names should only contain alphabetical characters and spaces, and should not be blank |
PHONE |
Phone numbers should only contain numbers, starts with digit '6', '8' or '9', and should be 8 digits long |
Emails should be of the format local-part@domain and adhere to the following constraints: 1. The local-part should only contain alphanumeric characters and these special characters, excluding the parentheses,
(!#$%&'*+/=?`{}~^.-), 1 to 50 characters long 2. This is followed by a '@' and then a domain name. |
|
ADDRESS |
Addresses can take any values, should not be blank, and should be 1 to 50 characters long |
SALARY |
Salary should only contain integers with no spaces or commas |
OT HOUR |
Overtime hours should only contain numbers up to two decimal places with no spaces or commas |
OT RATE |
Overtime rate should only contain numbers up to two decimal places with no spaces or commas |
DEDUCTIBLE |
Deductible should only contain numbers up to two decimal places with no spaces or commas |
DEPARTMENT |
Department should only contain alphabetic characters and spaces, should not be blank, and should be 1 to 30 characters long |
MANAGER |
Manager should only contain alphabetic characters and spaces, should not be blank, and should be 1 to 50 characters long |
RATING |
Rating should only contain numbers between 1 to 10 |
FEEDBACK |
Feedback can take any values, should not be blank, and should be 1 to 65 characters long |
INDEX |
Refers to the index number shown by the staff list command, and must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … |
3.1. Viewing help : help
Format: help
3.2. Adding a staff: add
Adds a staff to SSENISUB
Format: add n/NAME [p]p/PHONE_NUMBER [p]e/EMAIL [p]a/ADDRESS d/DEPARTMENT m/MANAGER [t/TAG]…
| A staff can have any number of tags (including 0) |
Phone numbers and Email addresses are unique, you will not be able to add a new staff with a pre-existing Phone number or Email address within SSENISUB
|
Examples:
-
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John Street, Block 123, #01-01 d/Accounting m/Marcus Lim t/staff -
add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/81729817 d/Marketing m/Edmund Tan t/staff
3.3. Listing all staff : list
Shows a list of all staff in SSENISUB.
Format: list
3.4. Editing a staff : edit
Edits an existing staff in SSENISUB.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [s/SALARY] [oth/OTHOUR] [otr/OTRATE] [de/DEDUCTIBLES] [d/DEPARTMENT] [m/MANAGER] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com s/1000
Edits the phone number, email address, salary of the 1st staff to be91234567,johndoe@example.comand1000respectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/
Edits the name of the 2nd staff to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
3.5. Deleting a staff : delete
Deletes the specified staff from SSENISUB.
Format: delete INDEX
Examples:
-
list
delete 2
Deletes the 2nd staff in SSENISUB. -
find Betsy
delete 1
Deletes the 1st staff in the results of thefindcommand.
3.6. Selecting a staff : select
Selects the staff identified by the index number used in the displayed staff list.
Format: select INDEX
Examples:
-
list
select 2
Selects the 2nd staff in SSENISUB. -
find Betsy
select 1
Selects the 1st staff in the results of thefindcommand.
3.7. Giving feedback to a staff: feedback
Provides feedback for an existing staff in SSENISUB
Format: feedback INDEX fb/FEEDBACK
Examples:
-
feedback 1 fb/You are great!
Gives the 1st staff a feedback of "You are great!".
3.8. Rating a staff: rate
Rates an existing staff in SSENISUB
Format: rate INDEX r/RATING
Examples:
-
rate 3 r/8
Rates the 3rd staff of a rating 8.
3.9. Setting private fields: privacy
Sets the mentioned field into a private field (displays as 'private' on staff panel).
Format: privacy INDEX [p/ y or n] [e/ y or n] [a/ y or n]
Examples:
-
privacy 1 p/y a/n
Sets thePhonenumber andAddressof the 1st staff in SSENISUB to private and public respectively. -
privacy 4 e/n p/n
Sets theEmailandPhonenumber of the 4th staff in SSENISUB to public.
3.10. Locating staff by name: find-n
Finds staff whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find-n KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
find-n John
ReturnsJohnandJohn Doe -
find-n Betsy Tim John
Returns any staff having namesBetsy,Tim, orJohn
3.11. Locating staff by email: find-e
Finds staff whose email contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find-e KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
find-e John@example.com
ReturnsJohn -
find-n Betsy@example.com Tim@example.com
Returns any staff having emailsBetsy,Tim
3.12. Locating staff by department: find-d
Finds staff whose department contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find-d KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
find-d Accounting
Returns any staff in Accounting DepartmentJohn -
find-d Accounting Tech
Returns any staff in Accounting or Tech DepartmentJohn,Betsy,Tim
3.13. Locating staff by manager: find-m
Finds manager whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find-m KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
Examples:
-
find-m John
ReturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find-m Betsy Tim John
Returns any manager having namesBetsy,Tim, orJohn
3.14. Sorting all staff by name : sort
Sorts the staff list by name.
Format: sort
3.15. Sorting all staff by department : sortDept
Sorts the staff list by department.
Format: sortDept
3.16. Sorting all staff by rating : sortRatingDown
Sorts the staff list by rating from highest to lowest.
Format: sortRatingDown or sortRating
3.17. Sorting all staff by rating : sortRatingUp
Sorts the staff list by rating from lowest to highest.
Format: sortRatingUp
3.18. Favouriting a staff : favourite
Favourites the specified staff and moves it up to the top of the list.
Format: favourite INDEX or fav INDEX
Examples:
-
list
favourite 2
Favourites the 2nd staff in SSENISUB. -
find Betsy
fav 1
Favourites the 1st staff in the results of thefindcommand.
3.19. Unfavouriting a staff : unfavourite
Favourites the specified staff and moves it up to the top of the list.
Format: unfavourite INDEX or unfav INDEX
Examples:
-
list
unfavourite 2
Removes the 2nd staff from favourite list. -
find Betsy
unfav 1
Removes the 1st staff in the results of thefindcommand from favourite list.
3.20. Listing entered commands : history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
3.21. Undoing previous command : undo
Restores SSENISUB to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Format: undo
|
Undoable commands: those commands that modify SSENISUB’s content ( |
Examples:
-
delete 1
list
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
select 1
list
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
3.22. Redoing the previously undone command : redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Format: redo
Examples:
-
delete 1
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command) -
delete 1
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies theclearcommand)
3.23. Counting the number of staff [coming in v2.0]: count
Count the number of staff in specific department in SSENISUB
Format: count d/DEPARTMENT
Examples:
-
count d/accounting
3.24. Locking SSENISUB [coming in v2.0]: lock
Locks SSENISUB with a specified password.
Format: lock PASSWORD
3.25. Unlocking SSENISUB [coming in v2.0]: unlock
Unlocks SSENISUB with a specified password.
Format: unlock PASSWORD
3.26. Authorization levels for features [coming in v2.0]: login, logout
Allows a user to log into the SSENISUB system with different authorization levels.
Format: login USERNAME PASSWORD, logout
Examples:
-
login AmyBee 123456 -
logout
3.27. Encrypting data files [coming in v2.0]
{explain how the user can enable/disable data encryption}
3.28. Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from SSENISUB.
Format: clear
3.29. Saving the data
SSENISUB data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
3.30. Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
4. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous SSENISUB folder.
5. Command Summary
-
Help :
help -
Add
add n/NAME [p]p/PHONE_NUMBER [p]e/EMAIL [p]a/ADDRESS d/DEPARTMENT m/MANAGER [t/TAG]…
e.g.add n/James Ho p/91829309 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 d/Accounting m/David Choo t/staff -
List :
list -
Edit :
edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [s/SALARY] [oth/OTHOUR] [otr/OTRATE] [de/DEDUCTIBLES] [d/DEPARTMENT] [m/MANAGER] [t/TAG].. .
e.g.edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com oth/10 -
Delete :
delete INDEX
e.g.delete 3 -
Select :
select INDEX
e.g.select 2 -
Feedback :
feedback INDEX fb/FEEDBACK
e.g.feedback 1 fb/Excellent job! -
Rate :
rate INDEX r/RATING
e.g.rate 1 r/8 -
Privacy :
privacy INDEX [p/ y or n] [e/ y or n] [a/ y or n]
e.g.privacy 2 p/y a/n -
Find by Name :
find-n KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find-n James Jake -
Find by Email :
find-e KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find-e johnd@example.com -
Find by Department :
find-d KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find-d Accounting -
Find by Manager :
find-m KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find-m Moses Ben -
Sort by Name :
sort -
Sort by Department :
sortDept -
Sort by Rating from Highest to Lowest :
sortRatingDownorsortRating -
Sort by Rating from Lowest to Highest :
sortRatingUp -
Favourite :
favourite INDEXorfav INDEX
e.g.favourite 1orfav 2 -
Unfavourite :
unfavourite INDEXorunfav INDEX
e.g.unfavourite 1orunfav 2 -
History :
history -
Undo :
undo -
Redo :
redo -
Lock SSENISUB [coming in v2.0] :
lock PASSWORD -
Unlock SSENISUB [coming in v2.0]:
unlock PASSWORD -
Login SSENISUB [coming in v2.0] :
login USERNAME PASSWORD -
Logout SSENISUB [coming in v2.0] :
logout -
Clear :
clear -
Exit :
exit